 WiFi
(Wireless Fidelity)
is the leading communication protocol for Wireless Technology.
WiFi generically refers to any type of 802.11 networks. All
Products tested and certified as “WiFi Certified” by the WiFi
Alliance are interoperable
with each other. WiFi
(Wireless Fidelity)
is the leading communication protocol for Wireless Technology.
WiFi generically refers to any type of 802.11 networks. All
Products tested and certified as “WiFi Certified” by the WiFi
Alliance are interoperable
with each other.
802.11 Standards:
• 802.11a: 5 GHz, 54 Mbps
• 802.11b: 2.4 GHz, 11 Mbps
• 802.11d: Multiple regulatory domains
• 802.11e: Quality of Service (QoS)
• 802.11f: Inter-Access Point Protocol (IAPP)
• 802.11g: 2.4 GHz, 54 Mbps
• 802.11h: Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) and Transmit
Power Control (TPC)
• 802.11i: Security
• 802.11k: Measurement

802.11a and 802.11b/g Standards can be positioned
as follows:
802.11a: Maximum Wireless LAN
performance, 8 Channels, but works only in U.S. and Japan,
5 GHz band has less interference (at least initially)
802.11a wireless LANs will provide for 54 Mbps, the highest
data rate available. With eight channels, 802.11a wireless
LANs may be scaled to any size without concern for channel
re-use issues. The 5 GHz UNII bands are today un-occupied
by potentially interfering devices. On the other hand, initial
802.11a offerings will not be compatible with ETSI regulations
for the EMEA market and some portions of the Asia Pacific
theater. As it operates in the 5GHz portions of the frequency
spectrum, 802.11a products are not compatible with the installed
base of 802.11b products. So, while 802.11a presents a number
of advantages over 802.11b, but it is not without its shortcomings
on an application by application basis.
802.11b/g:
data rate of 11Mbps - 54Mbps, works
worldwide.
802.11g is compatible with installed 802.11b networks, Wide
selection of client devices, Lower cost products, Lower power
products (important for handhelds).
802.11b has 3 Channels wireless
LANs and provide for an 11Mbps data rate, roughly that of
standard Ethernet and well less than that of 802.11a.
802.11g
has 11 Channels wireless LANs and provide for an 54Mbps data
rate at 2.4GHz.
802.11b/g products operate in
a portion of the frequency spectrum that has been set aside
for unlicensed operation on a worldwide basis. There is a
substantial and growing base of products installed today using
the 802.11b/g standards. The
lower power consumption of 802.11b/g,
longer range and generally lower cost relative to 802.11a
make 802.11b/g an attractive
option particularly for applications where the premium is
placed upon client battery life, size and cost.
By providing wireless LAN product
lines that covers both 802.11a
and 802.11b/g, SANTEC
Communications is able to better meet the largest
variety of today’s wireless networks application requirements.

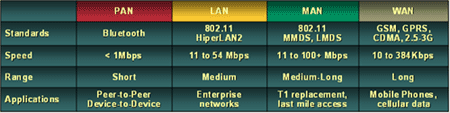
There are a number of wireless technologies available
on the market today:
- Wireless PAN (Personal Area
Network)
- Wireless LAN (Local Area
Network)
- Wireless MAN (Metropolitan
Area Network)
- Wireless WAN (Wide Area
Network)
I n t
e r c o n n e c
t i n g t h e
W o r l d |

 Home
Home Support
Support Products
Products Services
Services Partners
Partners Solutions
Solutions Contact Us
Contact Us 









